How to Write Advanced AI Prompts for Video Generators
Over two-thirds of social media users engage with AI-generated videos daily, making strong prompt-writing essential for standing out.

From music videos to cinematic short films, AI video generators can create dynamic content in seconds. But the quality of what you get depends almost entirely on the prompt you write. A vague prompt may lead to choppy, "AI-slop" results, while a well-crafted one can unlock polished, cinematic sequences that feel intentional and professional.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to write advanced AI prompts for video generation. You’ll learn the core elements every strong video prompt needs — like composition, atmosphere, and creative direction — as well as advanced strategies such as image-to-video workflows, camera movement control, and multi-shot sequencing. Along the way, we’ll share examples, templates, and tips you can use right away to make your AI-generated videos more consistent, stylized, and cinematic.
Table of Contents
What is an AI Prompt?
An AI video prompt is a written instruction you give to a video generator to guide what it produces. The quality of your prompt directly shapes the pacing, style, and clarity of the final video.
Simple prompts generate basic results, often vague or inconsistent. More detailed prompts, on the other hand, let you control key aspects like style, mood, and perspective, bringing the output much closer to what you envisioned.
For example, if you’re creating a music video and use the prompt “a band playing onstage”, you'll get a clip like the one below. It works on a literal level but lacks the style and energy you’d expect from an actual music video.
An AI-generated video of a band performing, created from a basic video prompt.
To make the scene feel like it belongs in a music video, you need to guide the AI with details such as lighting, character, energy, or even the camera style. These elements transform the same concept into a dynamic, stylized sequence.
For instance, using the prompt below produced a scene that is much more fitting for a music video:
“A cinematic opening shot of a rock band performing on stage in a packed underground club. The camera begins with a wide angle, capturing the glowing neon signs behind the stage and the crowd’s silhouettes raising their hands. Rain from the ceiling sprinklers glistens in the colored spotlights, catching blues, purples, and reds. The lead singer leans into the microphone, hair damp, as the guitarist strikes a chord that sends a ripple through the crowd. Smoke machines fill the stage with haze, giving the whole scene a raw, atmospheric, music-video quality that feels both gritty and electrifying.”
An AI-generated video of a band performing from an advanced video prompt.
Key Elements of an Advanced AI Video Prompt
When crafting an advanced AI prompt for images or videos, the details you include determine how polished, consistent, and professional the final output looks.
Here’s an overview of the main elements to consider: Composition, Atmosphere, and Creative Direction.

Composition
In advanced AI prompts, composition defines what your viewer sees and how they see it. Key elements include:
- Subject: The focus of the scene. This might be a product, person, or place.
- Frame: How much of your subject is visible. Specifying the frame controls how much of the subject and its surroundings is shown.
The frame of your image dictates how much of the subject and atmosphere is visible.
- Angle: The position relative to the subject. Specifying the angle changes how the subject appears; low angles make it look bigger and vice versa.
- Camera Movement: The way the virtual camera moves. This controls how the subject and scene is revealed, followed, or emphasized.
The camera movement changes how the scene is revealed.
Atmosphere
In advanced AI prompts, atmosphere sets the context and mood of the scene. Key elements include:
- Lighting: How your video is lit. This might describe the time of day (night, sunset), the light's temperature (warm, cool), or direction (backlit, front-lit).
Specifying lighting sets the mood of your video. For example, warm light sets a drastically different scene than cool fluorescent light.

- Background: The setting that surrounds your subject. It dictates what appears behind the subject, but it also influences the atmosphere of the video.
For example, a neon-lit city street will naturally cast dramatic shadows, while a sunset beach will add warm golden tones.

Creative Direction
In advanced AI prompts, creative direction defines the output's artistic vision. Key elements include:
- Visual Style: The overall artistic approach that determines the medium and execution of the output. This could be the format (animation, photorealistic) or the treatment of the subject (romantic, cinematic, surreal)
Cultural/Artistic Influences: The influences that inspire the output.
Unlike visual style, which is more general, influences are based on an artistic tradition or cultural mood. This might include references to media (The Simpsons, anime, Pixar cartoons) or art (impressionism, modern, abstract).
Referencing influences is one of the easiest ways to upgrade your AI prompts, with some of the most popular prompts being recreations of famous artists, directors, or franchises.
Narrative/Conceptual Notes: Even a short clip benefits from a hint of story — is the subject arriving, transforming, escaping, or celebrating? A narrative anchor makes the video feel intentional.
How to Write Advanced AI Prompts for Video Generators
1. Start with an Image and Expand It into Video
One of the most effective strategies for AI video generation is to use an image-to-video workflow rather than generating video directly from text.
Writing a text-to-video prompt can be difficult because it can be unpredictable, often producing outputs that are less stylized. By contrast, starting with image-to-video is easier because you can focus on the look and style of the scene before adding motion.
Imagine you’re creating the opening scene of a cyberpunk anime. Here’s what that prompt might look like:
Example Advanced AI Prompt for Text-to-Video
"A 90s anime-style cyberpunk city scene with two main characters - a girl with pink hair and a guy with blue hair. Retro-futuristic aesthetic, with neon lights and rain-slicked streets. The blue-haired and pink-haired characters will be leaning against a rusted metal wall, smoking. The lighting emphasizes the neon glows reflecting off wet pavement, and the characters have that classic anime facial expression—slight smirks, half-lidded eyes.
The retro-futuristic style should feel hand-painted, with muted pastel tones and visible film grain.
The girl lights her cigarette first, cupping her hand against the rain, then leans forward to share the flame with the boy. Their exchange is wordless, framed as a moment of quiet solidarity. He exhales, and the smoke mingles with hers, drifting toward the neon haze above. Behind them, a holographic sign flickers, briefly revealing the silhouette of a flying vehicle overhead."
This prompt was run to create the video below.
The output includes several inconsistent or even nonsensical details, and the overall style feels fairly plain, closer to a generic animation than the highly stylized cyberpunk look the prompt was aiming for.
Text-to-video output: characters generated, but style and details inconsistent with the prompt.
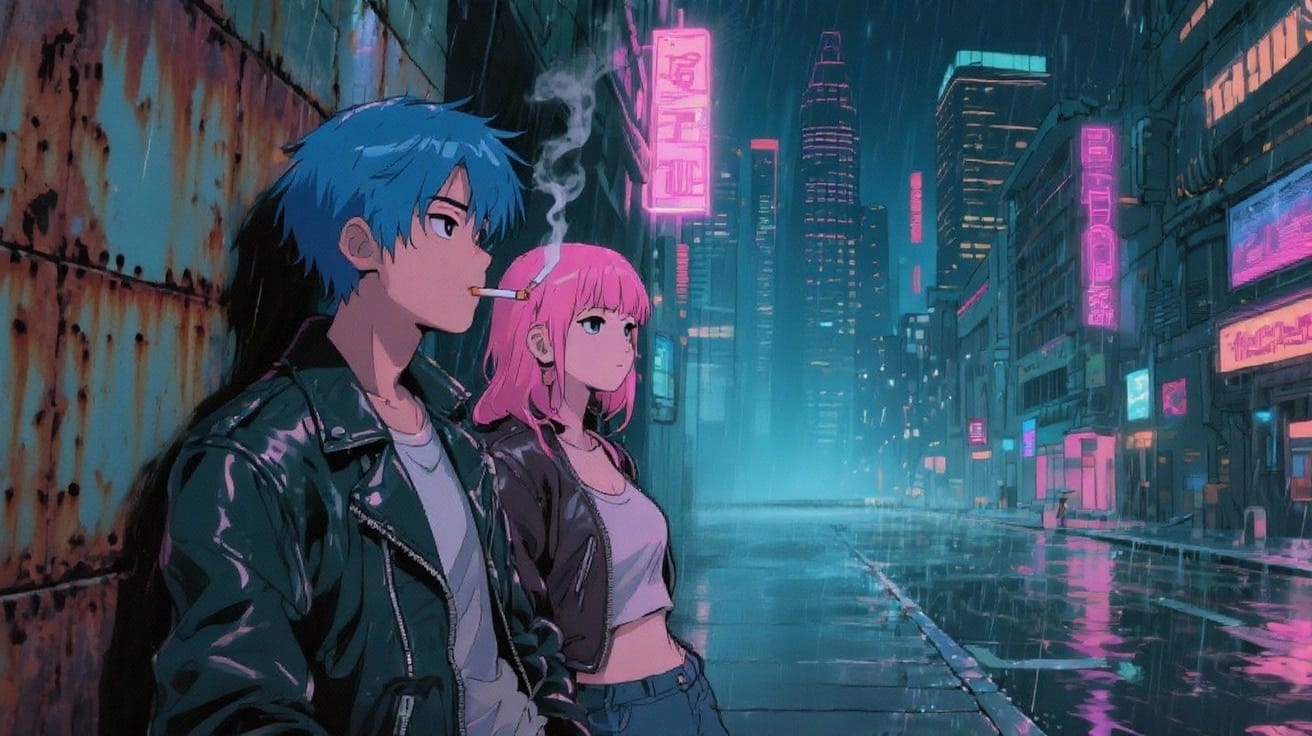
Now let’s try the same idea with an image-to-video workflow. First, we used the opening part of the prompt to generate a still image.
This locked in the characters and setting, producing a result that was much more stylized and visually consistent.
Example Advanced AI Prompt for Image
A 90s anime-style cyberpunk city scene with two main characters - a girl with pink hair and a guy with blue hair. Retro-futuristic aesthetic, with neon lights and rain-slicked streets. The blue-haired and pink-haired characters will be leaning against a rusted metal wall, smoking. The lighting emphasizes the neon glows reflecting off wet pavement, and the characters have that classic anime facial expression—slight smirks, half-lidded eyes.

Next, the prompt was expanded with instructions for motion, turning the static image into the video below.
While a few small inconsistencies remain, the overall result is far more stylized and detailed than the text-to-video attempt. The movement also feels more intentional, flowing naturally from the established scene rather than appearing random or out of place.
Example Advanced AI Prompt for Image-to-Video
The girl lights her cigarette first, cupping her hand against the rain, then leans forward to share the flame with the boy. Their exchange is wordless, framed as a moment of quiet solidarity. He exhales, and the smoke mingles with hers, drifting toward the neon haze above. Behind them, a holographic sign flickers, briefly revealing the silhouette of a flying vehicle overhead.
Expanded from the still: the second part of the prompt turns the image into a video sequence.
2. Direct Your Generations with Camera Movements
Camera work is one of the key elements that make videos feel cinematic. Without specifying movements, AI models often default to static shots. By adding film terminology into your prompts, you can guide how the camera moves and create sequences that feel choreographed rather than random.
Here are some of the most useful movement types to know:
- Pan: A sweep of the camera along a single axis.
- Tilt: A vertical movement, shifting the frame up or down.
- Dolly: Moving the camera forward or backward. This draws the viewer closer or farther from the subject.
- Truck: A lateral movement of the camera left or right.
- Roll: Rotating the camera around the lens axis, so the frame tilts diagonally.
- Pedestal: Physically moving the camera up or down without tilting the angle.
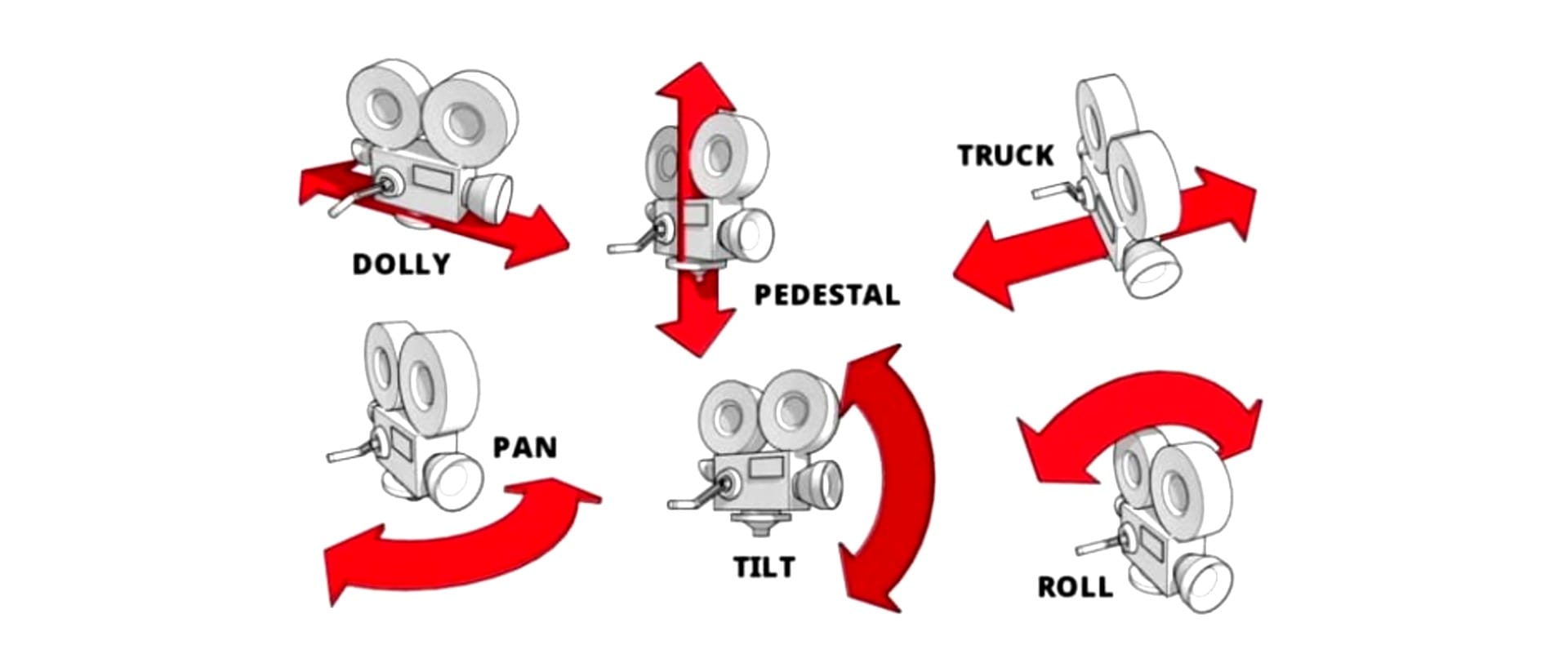
To make prompts more precise, combine a movement type with a pace modifier (slow, quick, gradual) and a target focus (subject, object, or environment). This gives you control over how the shot unfolds:
"Expand this image into video with a [pace] [movement type] on the [focus]. Then [describe the next movement or transition]."
If we applied this technique to the image-to-video generation above, this might look something like:
“Expand this image into video with a slow dolly in on the pink-haired girl, who is handed a cigarette by the guy. The video zooms in on her mouth as she starts smoking the cigarette. This is followed by a tilt up to the neon skyline.”
3. Build Multi-Shot Sequences with Continuity
Multi-shot prompting strings together different camera angles and focal points, much like how a scene is cut in traditional filmmaking. Instead of producing a single continuous shot, you can break the action into multiple perspectives.
Only some models support multi-shot prompting, and each may use different commands. For example, Kapwing uses the Seedream model, which recognizes the phrase “switch camera” as a signal to cut to a new shot.
Adding it to your prompt keeps the same setting and characters. You just specify a new angle, shot type, or action, and the model continues the sequence.
When writing multi-shot prompts, it helps to storyboard the way a filmmaker would:
- Start broad with a wide establishing shot to set the scene.
- Move into medium shots for character action or dialogue.
- Finish with close-ups to highlight key details or emotion.
We applied this technique to the shot below, expanding on the image-to-video workflow:
Example Advanced AI Prompt for Multi-Scene Generation
“Wide establishing shot of a neon-lit alley, rain falling across puddles. (switch camera) Medium close-up of a pink-haired girl lighting a cigarette, smoke drifting across the frame. (switch camera) Over-the-shoulder shot of a blue-haired boy watching her, neon signs flickering in the background. (switch camera) Extreme close-up of the cigarette ember glowing as neon reflections ripple across the wet pavement.”
This clip works because the layered structure makes the sequence feel intentional and narrative — something often missing from single-shot AI-generated content. The wide establishing shot sets the scene, the medium shots carry the action, and the close-up delivers an emotional payoff.
If the AI video generator you're using doesn’t support this feature, you can still apply the same techniques by generating each shot separately. The tradeoff is that style, characters, and setting may shift between generations, whereas multi-shot prompting helps preserve consistency across the entire sequence.
How To Tailor Your Advanced AI Video Prompts to the Right Model
Once you’ve mastered the core elements of advanced prompting, the next step is understanding how different AI video models interpret prompts. Each benchmark model has distinct strengths and should be used accordingly.
Below is a breakdown of some of the most popular AI video models, their capabilities, and how those strengths should shape your prompting strategy:
Sora 2
Sora 2 is good at understanding the intent of a prompt, handling story logic, continuity, and cause-and-effect better than other models. But it’s less responsive to detailed descriptions; overloading the prompt with instructions can confuse it.
Sora 2 is not designed for realism/cinematic clips. Best for simple storytelling, especially social media optimized clips
Prompting Tips:
- Keep prompts conceptual and scenario-based. Don’t over-specify visual details or camera moves.
- Include details on the desired feel of your video. Using words like 'funny', 'dramatic', or 'serious' goes a long way in Sora 2 prompts.
- If your concept includes multiple scenes, be sure to explicitly state that in the prompt. Sora can handle scene switches, but it won’t add them unless you specify it.
Example Sora 2 Prompt
A short video of a dog learning to ride his bike but accidentally winning the Tour De France.
An example Sora 2 video that I generated with the above prompt.
Veo 3 (Google)
Veo is best for generating realistic clips that look polished and cinematic, handling lighting and environment well.
It’s not well-suited for complex camera movement or abstract visuals. High-angle shots in particular often break or produce odd results. Veo works best with static framing or very simple camera actions, like a slow zoom or dolly-in.
Prompting Tips:
- Make sure to plan for sound. Veo always generates audio, so if you don’t want spoken dialogue or noise, specify background ambiance in your prompt.
- Be extremely descriptive. Include details about lighting, textures, atmosphere, and how the subject moves or interacts with their environment.
- Use simple camera moves only. If you want movement, keep it to slow zooms, or dolly shots. Avoid high angles, sweeping shots, or complex choreography.
Example Veo 3 Prompt
A static, eye-level shot of a man sitting beneath a large oak tree in a quiet park during golden hour. Warm sunlight filters through the leaves, creating dappled patterns across the grass and his clothing. He wears a light linen shirt and slowly turns the pages of a hardcover book resting on his lap. A breeze moves the branches above him. In the background, the park fades softly out of focus, with distant trees and a walking path barely visible. Ambient sounds of rustling leaves, birds chirping, and faint wind fill the scene. The camera remains steady throughout
An example Veo 3 video that I generated with the above prompt.
Seedance Pro
Seedance generates clips that feel more like casual phone footage than cinematic or hyper-realistic video. It’s best for simple, straightforward scenes with minimal subjects and limited detail. The overall look is lower fidelity than other models, with a softer or more generative feel.
While it can handle basic camera movement decently, it often struggles with logic and spatial continuity, so scenes often lack narrative cohesion. Text rendering is inconsistent, and Seedance does not support audio.
Prompting Tips:
- Keep prompts minimal. Use simple subjects and avoid dense scene setups or multiple characters.
- Avoid logic-dependent scenes. Don't expect coherent action sequences or clear cause-and-effect.
Example Seedance Pro Prompt
A realistic, cinematic, and wide shot video of black cat running alongside a flying bird through a field on a farm in the countryside. The sun is shining and in the distance, there is red farmhouse.
An example Seedance Pro video that I generated with the above prompt.
Kapwing Video 1
Kapwing V1 is a relative jack of all trades for video generation. Generated clips are highly realistic subjects tend to act logically. Kai V1 clips are best used as pieces in longer videos since they are typically cinematic, but unable to handle multi-scene generations or continuous plot lines.
Overcomplicated clips, like downtown environments or text-heavy scenes are prone to errors.
Prompting Tips:
- Think in cinematic moments, not story arcs. Use Kai V1 to generate short, high-quality scenes you can cut together manually.
- Keep the shots simple. It is best to avoid very dynamic clips with many subjects doing different shots. Rather, focus on detailing 1-2 subjects.
Example Kapwing Video 1 Prompt
A medium-wide cinematic shot of a man and woman standing on the rooftop of a tall building in a modern city during golden hour. The skyline stretches behind them, bathed in warm, amber light as the sun dips toward the horizon. The couple is holding hands and looking at the city. Their silhouettes are softly rim-lit by the sun, casting long shadows across the rooftop.
An example Kapwing Video 1 video that I generated with the above prompt.
Higgsfield
Higgsfield is best for creating short clips with stylized visual effects. It’s not optimized for full scenes or long narratives.
Most users upload a photo into a prebuilt visual effect from Higgsfield’s gallery. The tool then applies this motion and style to the image, turning it into a short video clip.
Prompting Tips:
- You don’t need to describe the visual effect itself, but it helps to describe how the input image should change once motion is applied. For example: “the camera slowly pulls back to reveal a foggy mountain valley”.
- Avoid narratives or longe videos. Higgsfield isn’t built for storytelling; it’s strongest when focused on a single visual moment.
Example Higgsfield Prompt
This prompt was used for the Earth Zoom effect:
A young woman stands in a narrow alleyway in Japan, bathed in warm sunset light. The camera pulls away sharply, initiating a smooth and rapid zoom-out. It rushes upward through the alley, past glowing signs and lanterns, revealing the architecture of a Japanese city.
An example Earth Zoom Out video I created with Higgsfield and Kapwing
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do my AI-generated videos look random or inconsistent?
This usually happens when prompts are too vague — add specifics about style, lighting, and motion to anchor the model’s output.
How can I avoid strange or nonsensical details in AI video outputs?
Focus your prompt on the essentials, avoid overloading with conflicting descriptors, and refine iteratively with short test runs.
How do I make AI generated videos look more cinematic?
Use film language — such as wide establishing shots, close-ups, and slow dolly moves — and layer in lighting and atmospheric cues.
What’s the best way to create multi-shot sequences with AI?
Make sure that the model you are using supports this feature. Signal to the start of a new show with a command like “(camera switch)”.
How can I use camera movements in my AI video prompts?
You can specify moves like pan, dolly, tilt, or orbit to guide how the virtual camera reveals the subject and sets pacing.









